40. The watt-hour meter is ………. instrument.
(i) an integrating
(ii) an indicating
(iii) a recording
(iv) a transfer
Answer: (i) an integrating
41. Indicating instruments are assumed to be most accurate ……… part of scale.
(i) at beginnig
(ii) at finishing
(iii) at half of full
(iv) none of the above
Answer: (iii) at half of full
42. ………… meter will be the most sensitive.
(i) 50 mA
(ii) 100 µA
(iii) 50 µA
(iv) 1 µ A
Answer: (iv) 1 µ A
43. On a simple ohmmeter, the 0 Ω mark is ……… of the scale.
(i) far left
(ii) in the middle
(ii) far right
(iv) none of the above
Answer: (ii) in the middle
44. If a wattmeter connected in circuit gives down scale reading, then we normally change connections of
(i) current coil
(ii) potential coil
(iii) both current and potential coils
(iv) none of above
Answer: (ii) potential coil
45. A permanent magnet moving coil ammeter is connected in 50 Hz a.c. circuit in which 5A current is flowing. The meter will read
(i) 0 A
(ii) 5 A
(iii) 2.5 A
(iv) none of above
Answer: (i) 0 A
46. In the above question, if the meter remains connected in the circuit for sometime,
(i) meter pointer gives full-scale deflection
(ii) meter pointer starts oscillating
(iii) meter coil is burnt
(iv) none of above
Answer: (iii) meter coil is burnt
47. If in the above question, the frequency of a.c. 0.1 Hz, the pointer will
(i) rise from zero and then falls back
(ii) read zero
(iii) read full-scale
(iv) none of above
Answer: (i) rise from zero and then falls back
48. On a simple ohmmeter, the infinity Ω mark is …….. of the scale.
(i) far left
(iii) in the middle
(ii) far right
(iv) none of above
Answer: (i) far left
49. The instrument used in an ohmmeter is generally
(i) moving-iron type
(ii) hot-wire type
(iii) permanent magnetic moving coil type
(iv) Dynamometer type
Answer: (iii) permanent magnetic moving coil type
50. When the terminals of a series ohmmeter are open-circuited, the pointer reads
(i) zero
(ii) infinity
(iii) a high resistance
(iv) none of above
Answer: (ii) infinity
51. Out of the following, the most accurate measurement of unknown resistance will be by
(i) potentiometer
(ii) ohmmeter
(iii) voltmeter and ammeter
(iv) Wheatstone bridge
Answer: (iv) Wheatstone bridge
52. A 50 V range voltmeter has a sensitivity of 20 kΩ/V. The total resistance of the voltmeter is
(i) 2.5 k Ω
(ii) 0.4 k Ω
(iii) 10 k Ω
(iv) 1 M Ω
Answer: (iv) 1 M Ω
53. Voltmeter-ammeter method of measuring the value of resistance is used to measure if its value is
(i) very low
(ii) very high and moderate
(iii) cannot say
(iv) none of above
Answer: (ii) very high and moderate
54. In a dynamometer wattmeter, the moving coil is the
(i) current coil
(ii) potential coil
(iii) current coil or potential coil
(iv) none of the above
Answer: (ii) potential coil
55. Fig. 1 shows an ammeter, a voltmeter and a wattmeter connected in the circuit. The wattmeter will read
(i) upscale
(ii) down scale
(iii) data insufficient
(iv) none of above
Answer: (i) upscale
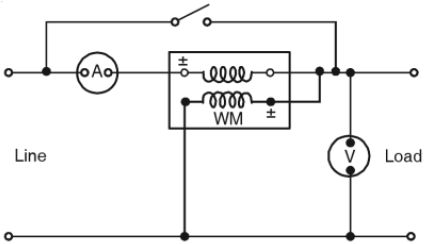
56. In the circuit shown in Fig. 1, the wattmeter reading will be
(i) equal to actual load power
(ii) less than actual load power
(iii) more than actual load power
(iv) none of above
Answer: (iii) more than actual load power
57. In Fig. 1, the ammeter reading will be
(i) equal to the load current
(ii) more than the load current
(iii) less than the load current
(iv) cannot be predicted
Answer: (ii) more than the load current
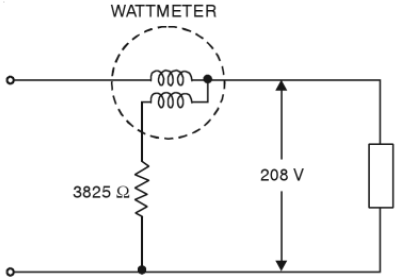
58. A dynamometer wattmeter with its voltage coil connected across the load side reads 192 W (See Fig. 2). The load voltage is 208 V and the resistance of potential coil is 3825 Ω. What is the true load power ?
(i) 125.8 W
(ii) 180.7 W
(iii) 224.6 W
(iv) 352.8 W
Answer: (ii) 180.7 W
59. In the above question, what is the percentage error due to wattmeter connection ?
(i) 6.25 %
(ii) 4.85 %
(iii) 11.34 %
(iv) 7.86 %
Answer: (i) 6.25 %
60. Induction wattmeter can measure
(i) a.c. power only
(ii) d.c. power only
(iii) both a.c. and d.c. power
(iv) none of above
Answer: (i) a.c. power only
61. To measure a.c. as well as d.c. power, we use
(i) induction wattmeter
(ii) dynamometer wattmeter
(iii) sometimes induction and sometimes dynamometer wattmeter
(iv) none of above
Answer: (ii) dynamometer wattmeter
62. In a single phase energy meter, braking torque is provided by
(i) permanent magnet
(ii) air friction
(iii) fluid friction
(iv) none of above
Answer: (i) permanent magnet
63. The full-scale deflection current of a permanent magnet moving-coil (PMMC) meter is 1 mA and the coil resistance is 50 Ω. The least voltage that can be measured with this meter is
(i) 50 mV
(ii) 25 mV
(iii) 100 mV
(iv) none of above
Answer: (i) 50 mV
64. If the full-scale current of a meter is 50 µA, then its sensitivity is
(i) 1000 Ω/V
(ii) 20,000 Ω/V
(iii) 10,000 Ω/V
(iv) data insufficient
Answer: (ii) 20,000 Ω/V
65. A 100 V. full-scale, 100 Ω/volt meter has a full-scale deflection current of
(i) 0.5 mA
(ii) 2 mA
(iii) 3.5 mA
(iv) 1 mA
Answer: (iv) 1 mA
66. A moving coil galvanometer has a sensitivity of 60 divisions/amp. When a shunt is used,its sensitivity becomes 10 div/amp. What is the value of the shunt used if the resistance of the galvanometer is 20 Ω ?
(i) 2 Ω
(ii)6 Ω
(iii) 4 Ω
(iv) 1 Ω
Answer: (iii) 4 Ω
67. Which of the following is likely to have the largest resistance ?
(i) moving coil galvanometer
(ii) voltmeter of range 10 V
(iii) ammeter of range 1 A
(iv) a copper wire of length 1m and diameter 3 mm
Answer: (ii) voltmeter of range 10 V
68. If 2 % of the main current is to be passed through a moving coil galvanometer of resistance G, the resistance of the shunt required is
(i) G/49
(ii) G/50
(iii) 49 G
(iv) 50 G
Answer: (i) G/49
69. A galvanometer has a resistance of G ohms. It is shunted by a resistance of S ohms. How much resistance should be added so that the main current remains unchanged ?
(i) S/(S + G)
(ii) G/(G + S)
(iii) SG/(G + S)
(iv) G2/(G + S)
Answer: (iv) G2/(G + S)